
Let’s build your chatbot today!
Launch a no-code WotNot agent and reclaim your hours.
*Takes you to quick 2-step signup.
Over the years, conversational AI has evolved from simple rule-based scripts into sophisticated AI-driven interactions. Businesses are now moving beyond traditional chatbots to adopt AI agents, but what exactly sets these two apart?
Chatbots were once the cutting edge of AI-driven customer interaction. They helped businesses automate responses, provide 24/7 support, and reduce operational overhead. But in 2025, chatbots are no longer the endgame.
Enter AI agents—more advanced, intuitive, and capable of responding, thinking, learning, and executing tasks independently. These AI agents come with advanced capabilities, allowing them to perform complex tasks, adapt to changing requirements, and integrate seamlessly with various systems and applications.
So, in the battle of AI agent vs chatbot, which one wins? Is it time to ditch chatbots, or do chatbots still hold their ground? Let’s break it down.
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Understanding the basics
As AI becomes a business necessity rather than a novelty, understanding the AI agent vs chatbot debate is more important than ever. Both use conversational AI, but there are some key differences. While chatbots are excellent at handling structured interactions, AI agents push the boundaries with advanced automation, contextual learning, and decision-making capabilities. AI agents offer more advanced capabilities than traditional AI chatbots, particularly in handling complex tasks and automating multi-step workflows. But which one is the right fit for your business? Let’s break it down.
What is a chatbot?
AI agents and chatbots might seem similar, but they serve very different roles. Chatbots stick to scripts for quick, structured responses, while AI agents adapt, learn, and automate complex tasks. Understanding these differences is key to optimizing customer interactions. For instance, businesses looking to enhance support quality should explore how AI can improve customer experience by leveraging adaptive AI solutions. Knowing when to use each can make all the difference in customer experience.
A chatbot, or AI chatbot, is a software application designed to simulate human conversation through text or voice interactions. Businesses deploy AI chatbots primarily to automate customer interactions, streamline processes, and provide instant responses.
There are two primary types:
Rule-based chatbots: Think of these as glorified decision trees. They follow pre-programmed flows and scripts, handling predictable and structured interactions. Great for simple queries, but the moment a user goes off-script, things fall apart.
AI-powered chatbots: These chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand user intent and generate relevant responses. Examples include AI chatbots used for customer support, such as lead-generation chatbots.
While chatbots are widely used in customer support chatbots, lead generation, and simple e-commerce interactions, they do come with limitations.
AI-powered chatbots, especially those trained on large language models (LLMs)—bring a more advanced conversational ability. They can recognize user intent, generate more human-like responses, and even offer personalized recommendations.
But chatbots, even AI-powered ones, have limitations. They struggle with multi-turn conversations, lack deep context awareness, and are ultimately reactive—they wait for user input before responding. They can’t execute complex workflows or make autonomous decisions. That’s where AI agents take over.
Chatbot use cases
Chatbots excel at automating basic tasks, offering quick responses, and efficiently handling high-volume customer inquiries efficiently. They shine in industries where structured interactions and predefined workflows are sufficient.
E-commerce Industry: Shopping online should be seamless, and chatbots help make that happen. They announce daily offers directly in the chat window, personalizing deals based on browsing history or past purchases.
Healthcare Industry: Healthcare never sleeps, and healthcare chatbots ensure support is always available. They streamline appointment booking, matching patients with doctors or scheduling procedures in real-time.
Insurance Industry: Despite being a trillion-dollar industry, insurance remains complex and often overwhelming for customers. A well-designed insurance chatbot can break down policies, clarify processes, and make offerings easier to navigate.
What is an AI Agent?
If chatbots are digital assistants, AI agents are digital workers. They don’t just answer questions—they think, decide, and act, significantly enhancing business processes.
AI agents operate on an entirely different level:
They analyze context dynamically, meaning they don’t just process one-off queries—they remember previous interactions and build responses accordingly.
They leverage deep learning and large language models (LLMs), allowing them to understand tone, sentiment, and intent beyond surface-level text.
They automate workflows, taking over complex, multi-step processes across different platforms and systems.
They improve over time, continuously learning from previous interactions to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Unlike chatbots, these systems don’t just respond—they handle entire workflows. Imagine a customer asking about a refund. A chatbot might provide a link to refund policies, while this system would initiate the refund, verify account details, ensure AI compliance, update the CRM, notify finance, and send a confirmation email—all autonomously.
AI Agent use cases
E-Commerce: AI agents don’t just suggest products; they manage inventory, process payments, and coordinate logistics. A customer buying a laptop? The AI agent confirms stock, initiates payment, schedules delivery, and sends tracking updates. Using the best merchant services helps ensure secure, seamless transactions for a smoother customer experience.
Healthcare: Instead of giving generic health tips, AI agents schedule doctor appointments, pull patient records from customer data, and follow up with post-visit reminders. Imagine a patient asking about a recurring symptom—an AI agent could cross-check medical history and suggest next steps.
Banking & Finance: AI agents are transforming digital banking by handling fraud detection, approve transactions, and assisting customers with financial planning. A user inquiring about a suspicious transaction? The AI agent scans account activity, flags anomalies, and suggests next steps, reducing reliance on human analysts.
The takeaway? AI agents aren’t just responding to customer needs—they’re orchestrating actions across systems, making businesses faster, smarter, and more efficient. Specially designed and trained AI platforms can generate real time reports on financial performance of the business especially SaaS based businesses.
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Key differences
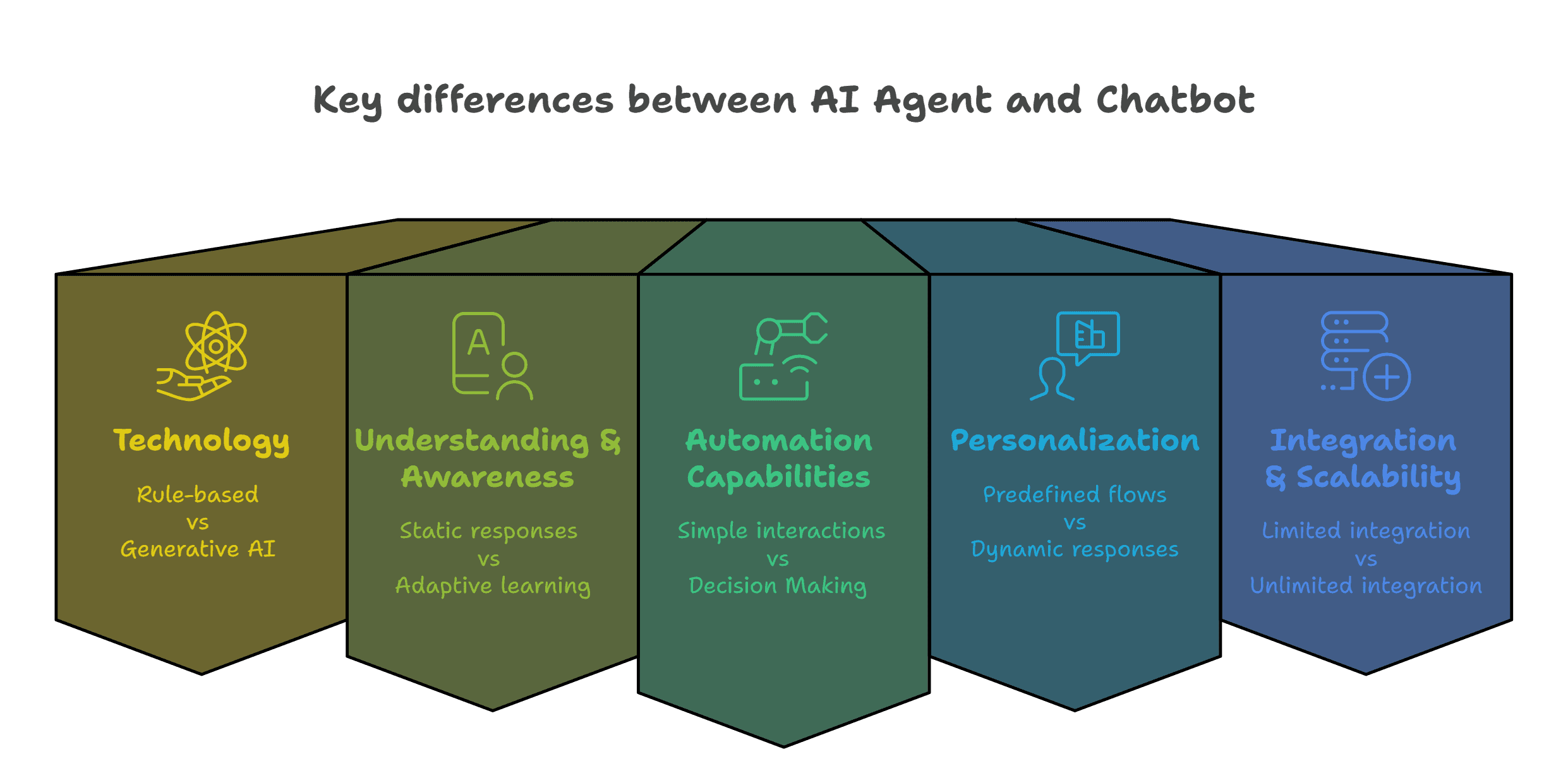
AI chatbots and AI agents both operate on artificial intelligence, but they aren’t the same thing. At first glance, they seem similar—they both interpret what you say, process the request, and generate a response. But the deeper you go, the clearer the distinctions become. AI agents leverage advanced machine learning models, including deep learning and reinforcement learning, to perform complex tasks with minimal human guidance. These models enable AI agents to learn from interactions and adapt their behavior, which contrasts with traditional systems that have limited learning capabilities.
1. Technology: Rule-Based vs. Generative AI and LLMs
Chatbots primarily rely on rule-based systems, keyword matching, and predefined decision trees. They operate within a structured framework, offering scripted responses based on specific inputs. Even chatbots with basic machine learning capabilities remain constrained within predefined workflows.
AI agents, on the other hand, harness generative AI and large language models (LLMs) to interpret, process, and respond dynamically. They improve over time using deep learning, natural language understanding (NLU), and reinforcement learning, making them far more adaptable and intelligent than traditional chatbots.
2. Understanding & Context Awareness: Static Responses vs. Adaptive Learning
Chatbots rely on predefined responses and static scripts, which means they struggle with handling ambiguous, multi-turn conversations. They excel at structured interactions but lack true context awareness.
AI agents go beyond just responding to queries; they understand user intent, track past interactions, and adapt their responses accordingly. They can process multi-step interactions across different platforms and retain the memory of previous conversations to deliver more relevant responses.
3. Automation Capabilities: Simple Interactions vs. Task Execution & Decision-Making
Chatbots are primarily designed to assist users by answering FAQs or guiding them through predefined processes. They can handle routine inquiries but cannot execute tasks beyond their scripted scope.
AI agents are task-driven problem solvers. They don’t just provide information—they take action. They can automate workflows, make independent decisions, and complete tasks autonomously.
4. Personalization: Predefined Flows vs. Dynamic, User-Specific Responses
Chatbots follow a one-size-fits-all approach, offering responses based on fixed dialogue flows. While they can be programmed to recognize user preferences to some extent, their personalization capabilities are limited.
AI agents dynamically adjust their responses based on user behavior, preferences, and real-time data. They continuously refine their outputs, making interactions feel more natural and tailored to the individual.
5. Integration & Scalability: Limited vs. Deep Business Process Integration
Chatbots typically integrate with a limited set of databases or APIs to fetch information, making them suitable for basic customer interactions but not for complex business processes.
AI agents offer deeper integration across multiple systems, allowing them to interact with databases, CRMs, cloud services, and real-time data sources. This scalability enables businesses to deploy AI agents for end-to-end automation, decision-making, and process optimization.
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Where each excels
AI agents and chatbots might seem similar, but they serve very different roles. Chatbots stick to scripts for quick, structured responses, while AI agents adapt, learn, and automate complex tasks. Knowing when to use each can make all the difference in customer experience.
When to use a chatbot
Chatbots shine in scenarios where speed and efficiency matter more than depth. They are best suited for structured interactions that don’t require deep context.
Basic Customer Service & FAQs: Chatbots are ideal for handling basic tasks such as common queries like business hours, return policies, or troubleshooting steps. A chatbot in retail can instantly respond to “Where is my order?” without involving human agents, reducing customer wait times.
Lead Generation & Form Filling: Chatbots guide website visitors through a seamless lead-capturing process. For instance, real estate firms use chatbots to ask potential buyers about location preferences and budget, automatically qualifying leads.
Simple E-Commerce Interactions: Chatbots assist users with product recommendations, order status updates, and return requests. Fashion brands use chatbots to suggest outfits based on a user’s style preferences, offering an interactive shopping experience.
Check out our step-by-step guide on how to create your own AI chatbot from scratch.
When to use an AI Agent
AI agents go beyond traditional chatbots - they take action. If your business requires automation, personalization, or multi-step workflows, an AI agent is the better fit.
Handling complex customer queries: AI agents can analyze previous interactions and customer history to provide detailed, context-aware responses. Healthcare providers use AI agents to help patients schedule appointments, suggest treatment options, and answer medical queries with real-time information.
Automating workflows across multiple systems: AI agents integrate with multiple platforms, reducing human workload. In banking, AI agents verify user identities, detect fraudulent transactions, and assist with secured loan approvals—all without human intervention.
Providing personalized recommendations: AI agents analyze user and customer data to offer personalized recommendations. Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify use AI agents to suggest content based on viewing or listening history, increasing engagement and retention.
Chatbots and AI agents are often confused, but they have distinct differences. Chatbots are typically rule-based systems that follow predefined scripts to respond to user inputs. In contrast, AI agents leverage machine learning models, including deep learning and reinforcement learning, to perform complex tasks with minimal human guidance.
Check out our step-by-step guide on how to build AI Agents.
AI Agent vs Chatbot: Which one to choose in 2025?

The decision between an AI agent and a chatbot isn’t just about technology—it’s about business goals, complexity, and cost. Chatbots are great for structured, repetitive tasks, while AI agents are designed for context-aware automation.
You can consider the below factors to find out what suits you the most.
Business Needs: If your business deals with high-volume, simple tasks and queries, a chatbot can handle the load. But if your workflows involve decision-making, integrations, and automation, an AI agent is a better choice.
Complexity: A chatbot can guide a user through basic troubleshooting, but an AI agent can diagnose issues and execute solutions across multiple platforms.
Budget: Chatbots are cost-effective for small businesses, while AI agents require higher investment but deliver long-term ROI through automation and efficiency.
Hybrid approach: Best of both worlds
Many businesses now rely on platforms like WotNot to create hybrid solutions that integrate both chatbots and AI agents for a seamless user experience. A chatbot can handle FAQs and basic customer support, while an AI agent takes over more complex queries.
Example: In e-commerce, a chatbot might assist customers with product searches and store policies. But once a customer needs order modification or a refund, an AI agent steps in to handle the process end-to-end without human intervention. These agents are designed to solve complex problems, execute multi-step plans and adapt their behavior autonomously to handle more challenging tasks.
If your business thrives on simple, high-volume interactions, a chatbot is the right fit. If automation, personalization, and decision-making are priorities, AI agents are the future. A hybrid approach brings the best of both worlds for those who want to balance cost and efficiency.
Conclusion
The line between chatbots and AI agents is blurring fast. AI agents are evolving to become the backbone of automated workflows, offering advanced capabilities such as performing complex tasks, adapting to changing requirements, and integrating seamlessly with various systems and applications. Meanwhile, chatbots continue to improve with better NLP and integration capabilities.
The real question isn’t “AI agent vs chatbot?”—it’s “How can they work together?”
If you want to future-proof your AI strategy, schedule a demo and explore how AI-driven automation can transform your business.
ABOUT AUTHOR


Hardik Makadia
Co-founder & CEO, WotNot
Hardik leads the company with a focus on sales, innovation, and customer-centric solutions. Passionate about problem-solving, he drives business growth by delivering impactful and scalable solutions for clients.

Start building your chatbots today!
Curious to know how WotNot can help you? Let’s talk.

Start building your chatbots today!
Curious to know how WotNot can help you? Let’s talk.



